Geotechnical and Groundwater Engineering
Staff
Research Topics
To safely and economically construct and maintain social infrastructure for the next generation, it is necessary to create a ground environment that considers the harmony between people and the global environment. To meet this demand, we are developing technology to measure and evaluate environmental conditions on the ground and groundwater in a simple and compact manner using such methods as ground surveying, in-situ testing, indoor soil testing, and numerical simulations. By accurately characterizing permeation values, mechanical properties of the ground, and soil structure, we are contributing to reducing ground disasters, and improving the ground environment in the future.
Field measurements and laboratory experiments to estimate parameters related to groundwater seepage and infiltration
Developing simple and compact ground surveying and in-situ testing methods
|
Because most ground disasters occur in the unsaturated region, soil tests and ground surveys on unsaturated soils have been performed to measure the geotechnical characteristics in an unsaturated state. In addition, because it is necessary to evaluate quantitatively the ground behavior at the time of ground disasters, the following two themes are proposed: (1) in-situ position testing on a local scale with simple and compact equipment, (2) ground scale surveying on a field scale using a non-destructive measurement method from the ground surface. These would evaluate the safety of levees and slopes. |
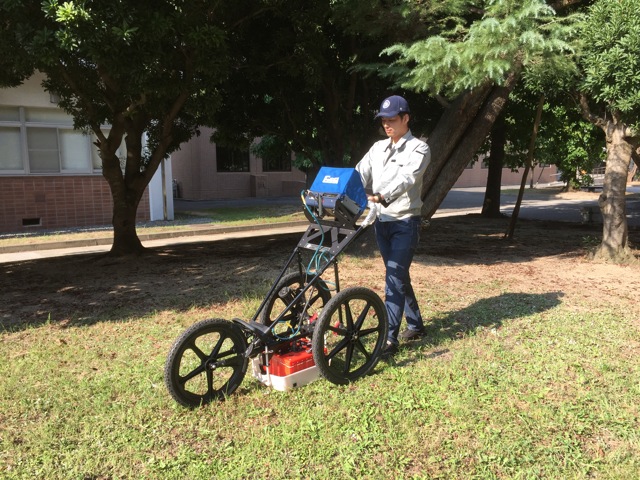

|
Developing monitoring and numerical modeling methods to assess the safety of levees in the context of failures caused by seepage flow
|
A monitoring method for soil water content and pore water pressure using the infiltration behavior of the river levee has been proposed. This method can be applied to the design and construction work of the river levee by appropriately evaluating the safety of river levee. A simulation model that can faithfully reproduce the measurement data based on saturation and unsaturated infiltration analyses is developed. |
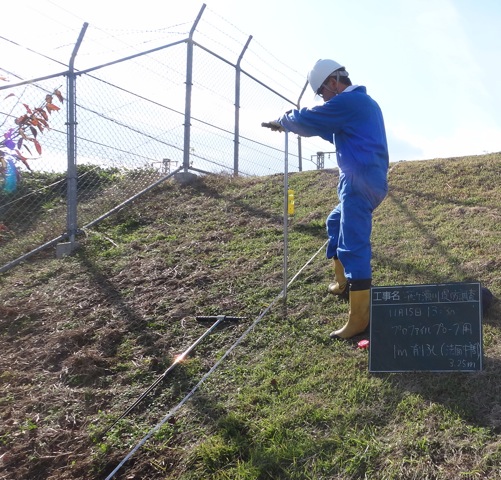

|
Evaluation of the shear strength and deformation characteristics of unsaturated soils
|
In order to prevent and reduce ground disasters in unsaturated earth structures (slope, levee, embankment, etc.) caused by a rainfall, it needs to grasp the failure mechanism of soil structures due to the rain infiltration. For this, the shear tests with the water retention test in the laboratory are carried out according to the confining stress state reproducing the state of ground as well as the deformation mode of soil structures. The shear strength and deformation characteristics of the soil structures are examined based on the obtained results. |
 |
Distinct element method (DEM) simulation of the shear behavior of soils
|
In general, it is difficult to measure the shear strength and deformation at the micro level, i.e., the soil particle level of a specimen in laboratory tests. Thus, 2D and 3D numerical simulations at the particle level are being conducted using the distinct element method (DEM) on the shear behavior of granular material (sandy soil) with water immersion. This research examines the mechanical characteristics of a granular material at the micro level, and we expect that this will continue to be a popular topic in geotechnical engineering in the future. |
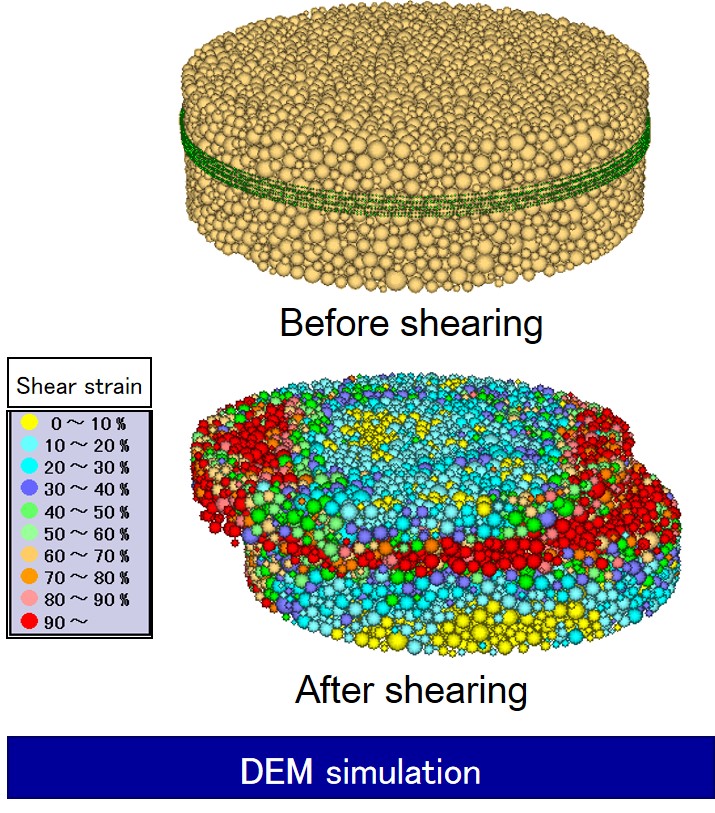
|
Safe and secure soil materials
|
In traditional ancestral Japanese building techniques there is a tapping method that applies a soil material by mixing slaked lime and "bittern" (MgCl2 · 6H2O)) or black coal to the soil to the house entrance. This is similar to a traditional compaction method. The soil materials were developed using room temperature solidification technology with lime-based fine powders without thermal energy. This would have an added value not found in natural ground materials and can address environmental preservation concerns, i.e., these are environment-friendly materials that naturally returns to the earth after enduring long-term use. |
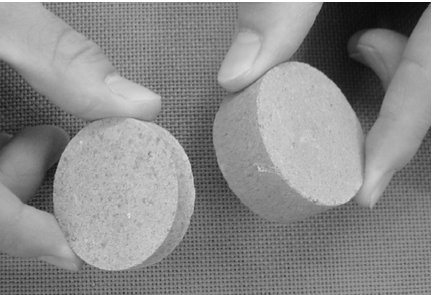
|
Applicability of water-repellent soil to overlayer of capillary barrier
|
This study focuses on the applicability of water-repellent soil to overlayer of the capillary barrier that has long-term shutoff and drainage functions. In order to examine the mechanical and hydraulic characteristics of water-repellent soil, the constant water content compression (CWCC) test and the water retention test are performed. Furthermore, the laboratory model test of the capillary barrier with the numerical analysis is also performed to verify the function of the new capillary barrier proposed in this study. |
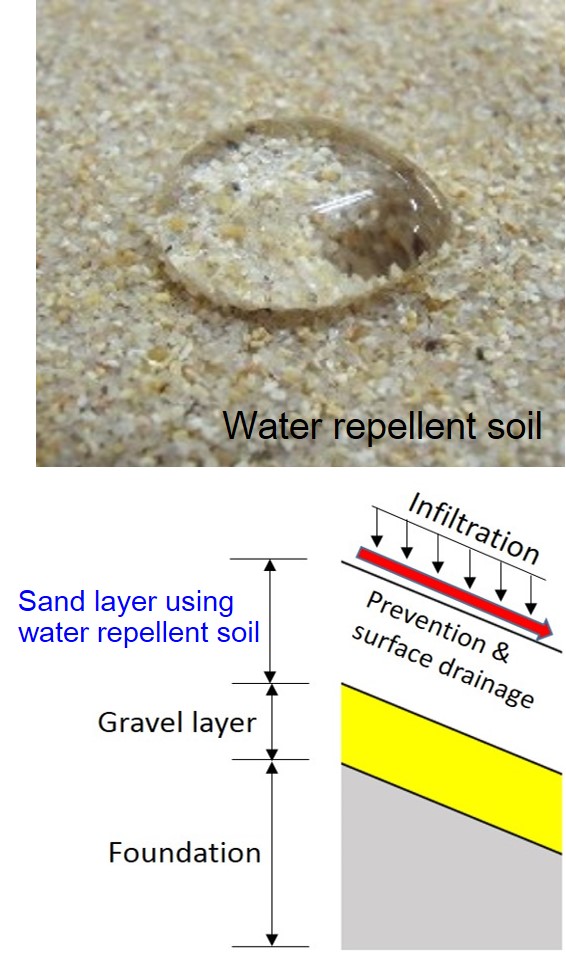
|
Developing a flexible and robust communication infrastructure system for a network of sensors used to remotely monitor damage during natural disasters
|
When a large-scale disaster occurs, it is crucial to have stable data transfer from a network of sensors. For a region considered as high-risk, it is essential that the sensor network and data communication infrastructure be installed and configured within several hours. This study aims to develop a novel sensor network and data communication system for a test site for monitoring slope stability during intense precipitation events. |
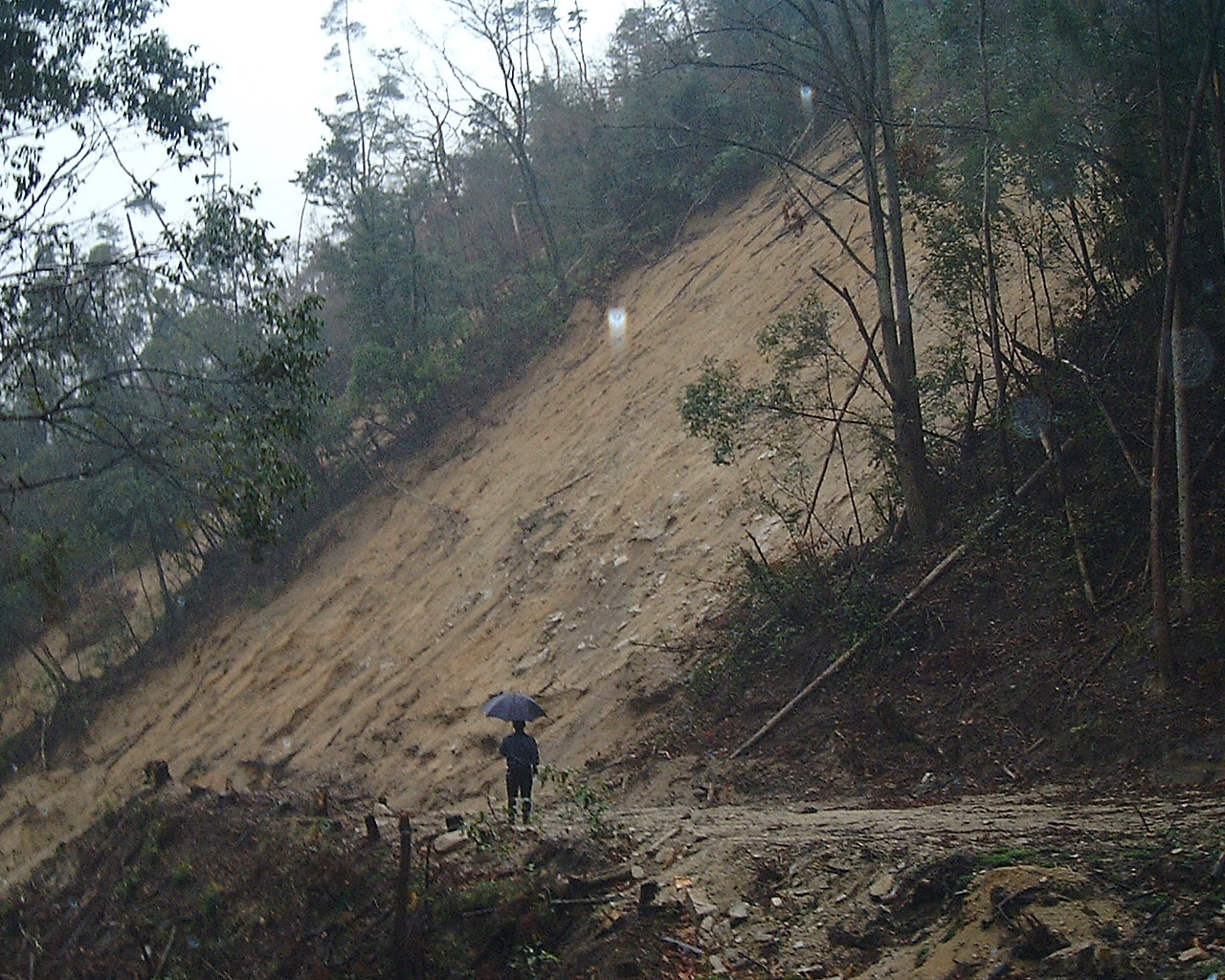

|
Establishing a technique for monitoring soil and groundwater contamination using Frequency Domain Reflectometry
|
The purpose of this study is to apply a measuring system for subsurface contamination; the FDR (Frequency Domain Reflectometry) and FDR-V (with Vector network analyzer) system are employed to measure salinity and oil contaminants. |
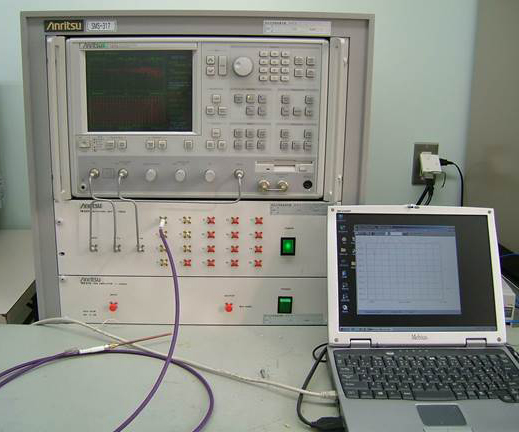

|
Publication List
- Y. TAKESHITA, H. SUWA and T. MORII. 2007. Field techniques for measuring hysteretic soil hydraulic properties of unsaturated sandy soils, Journal of JSCE, Dicision C, Vol.63 No.4, pp.1153-1162. (in Japanese)
- Y. TAKESHITA, T. OHYAMA, R.SAKONO and J.TAMURA. 2008. Experimental study on mechanical properties of ‘Tataki’ soil, Ground Engineering, Chugoku Branch of Japanese Geotechnical Society, Vol.26, No.1, pp.71-76. (in Japanese)
- Y. TAKESHITA, S. MORIKAMI, S. MORITA, S. KURODA and M. INOUE 2009. Non-destructive measurements of unsaturated seepage flow by using ground-penetrating radar, Journal of JSCE, Dicision C, Vol.65, No.4, pp.943-950. (in Japanese)
- Kim, B.S., Shibuya, S., Park, S.W., and Kato, S. 2013. Suction stress and its application on unsaturated direct shear test under constant volume condition. Engineering Geology, Vol. 155, pp. 10-18.
- Kim, B.S., Park, S.W., and Kato, S. 2014. DEM simulation on deformation mode and stress state for specimen shape in direct shear test. International Journal of Computational Methods, Vol. 11, No. 2, pp. 1342004-1~18.
- Y. TAKESHITA, B.S. KIM and T. MORII. 2015. Study on Techniques for Measuring the Field-Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity of Soils by Using Guelph Pressure Infiltrometer, Ground Engineering, Chugoku Branch of Japanese Geotechnical Society, Vol.33, No.1, pp.181-186. (in Japanese)
- Y. TAKESHITA. 2015. Field Techniques for Measuring Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated soils,The Japanese Geotechnical Society,Vol.63, No.8, pp.61-62. (in Japanese)
- Kim, B.S., Kato, S., Park, S.W., and Takeshita, Y. 2015. Effect of meniscus water on shear behavior for wettable and non-wettable unsaturated soils, Japanese Geotechnical Journal, Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 267-276.
- Kim, B.S., Kato, S., Park, S.W., and Takeshita, Y. 2016. DEM Simulation on Opening between Shear Boxes in Direct Shear Test, Japanese Geotechnical Journal, Vol.11, No.1, pp. 21-31.
- Kim, B.S., Park, S.W., Takeshita, Y., and Kato, S. 2016. Effect of suction stress on the critical state of compacted silty soils under low confining pressure. International Journal of Geomechanics, ASCE, D4016010-1-11.