Hydraulic Engineering
Staff
Research Topics
Water-related disaster prevention and mitigation
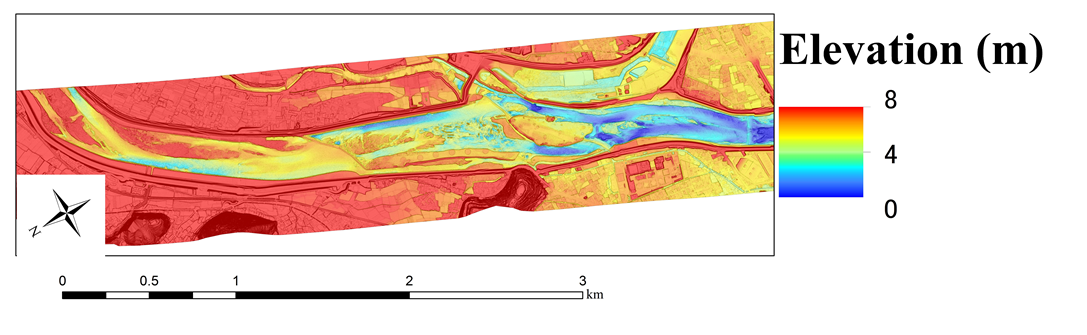
ALB measurements of channel bathymetry for river management
|
Recently, an airborne laser bathymetry (ALB) system using two types of simultaneously pulsed lasers (green and near infrared) has attracted the attention of river and coastal engineers for use as an efficient cost-saving surveying tool. This technology is effective for high-resolution measurements of planar bathymetry, including the underwater bed profile. For this study, we applied an ALB system and examined the accuracy in the targeted section by comparing ALB data at 2 m horizontal resolution with existing survey data obtained using the conventional method. Then, we evaluated the effects of using high-resolution ALB data in river flow analysis.
|
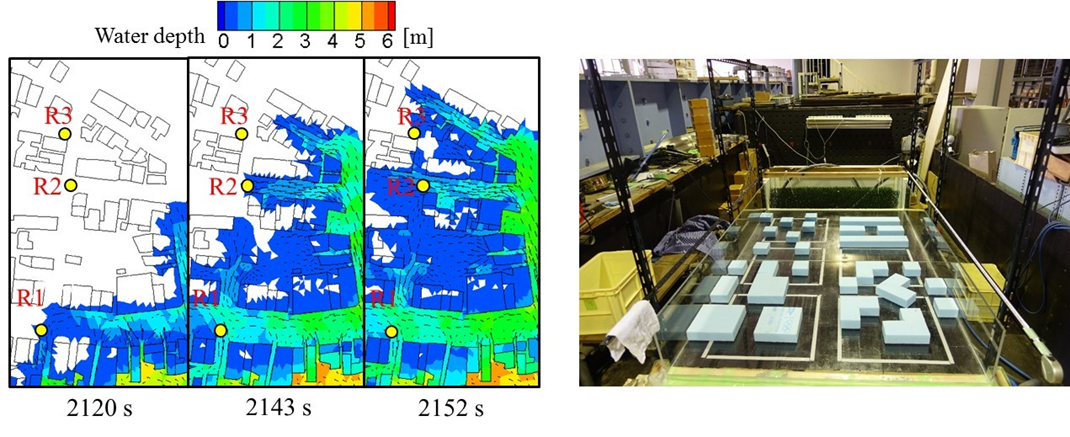
Developing practical numerical flood simulations in urban areas
|
Numerical simulations of floods in urban areas are useful for establishing evacuation programs and revising future city planning. In the present study, a set of shallow water equations was used to simulate the swift current on the streets to characterize horizontal flow diversion and concentration considering actual building configurations. The finite volume method was applied to an unstructured triangular mesh system to express the orientation and physical characteristics of each building based on a detailed city map. Recently, we conducted laboratory experiments and applications for actual events to develop more accurate and practical simulations of floods in urban areas.
|
Publication List
- K. Yoshida, S. Maeno, K. Mano, K. Yamaguchi, and R. Akoh (2017): Application of high-resolution ALB data of shallow water to river flow analysis, Proc. 3rd Int. Symp. on Shallow Flows, Eindhoven, NL.
- K. Yoshida, S. Maeno, R. Akoh, K. Yamaguchi, T. Iwaki, S. Fujita, Y. Hirai (2016): Improvement of diversion weir and surrounding vegetation condition effects on diversion discharge in the Asahi River, Proc. 20th IAHR-APD Congress, Srilanka.
- K. Yoshida, S. Ushijima, R. Tanaka, N. Miyagi, S. Maeno (2015): Numerical prediction of hydrodynamic force acting on a natural stone in open-channel flows, Proc. 36th IAHR World Congress, The Hague, the Netherlands.
- K. Yoshida, S. Maeno, S. Fujita, S. Matsuyama (2014): Prediction of forestaion process in the Asahi river, Japan using a vegetation dynamics model, Proc. 19th IAHR-APD Congress, Hanoi, Vietnam.
- R. Akoh, S. Maeno, S. Hirashita, K. Yoshida and T. Matsumoto (2016) : “Two-dimensional river bed configuration analysis of the Hii River and diversion channel flood in September 2013”, International Symposium on River Sedimentation, Stuttgart, Germany.
- R. Akoh, S. Maeno and K. Yoshida (2017) : “Improvement of float measurement method for river discharge using quasi-3D flood analysis”, 4th ISSF, Eindhoven, The Netherlands.
- R. Akoh, T. Ishikawa, T. Kojima, M. Tomaru, and S. Maeno (2017), “High-resolution modeling of tsunami run-up flooding: A case study of flooding in Kamaishi City, Japan, induced by the 2011 Tohoku Tsunami”, Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci., 17, 1871-1883.