Research Area : Solid Waste Management and Recycling

- Prof.
FUJIWARA Takeshi
Regional waste material recycling towards low carbon society:
Sanitary waste treatment is a fundamental in solid waste management, moreover, it is required that “from waste to material” and “from waste to energy” to mitigate green house gases emission. Solid waste processes, such as waste separation at source, segregated waste collection, optimal waste transportation, material and energy recovery treatment, and safe landfill disposal, should be combined appropriately so as to shorten the environmental burden. Our laboratory studies on designing methods to establish a sophisticated solid waste management that is suitable for sustainable regional society, specially in Asia.


Evaluation of the biomass waste recycling in university campus:
From view point of carbon neutral, biomass waste should be more utilized in a sound material-cycle society. By considering characteristics of various kinds of solid waste generated in our campus, such as kitchen waste, mowed grass, dead leaves, pruned branches, agriculture waste, animal dung in different seasons, our laboratory researches on effective biomass waste recycling methods.
Development of a disaster waste management training system:
Japan is exposed by many risks of natural disasters such as earthquake, land sliding, tsunami, flooding and so on. Once a big natural disaster comes like the Great East Japan Earthquake, a huge amount of disaster waste generates in a short period. In order to recover the town from the damage speedy, initial countermeasure actions for disaster waste treatment by local government are quite important. Therefore, our laboratory is constructing a knowledge base of the actions and also developing a training support system for the local government.

Research Area : Solid Waste Management and Recycling

- Assoc. Prof.
MATSUI Yasuhiro
Modeling on waste generation and discharge
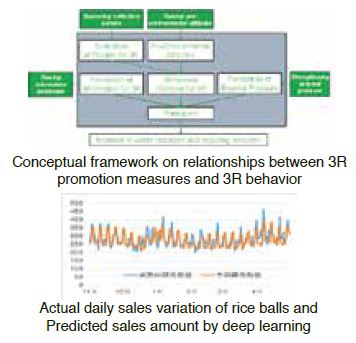
To support rational and effective decision making on municipal solid waste management toward sustainable society, our laboratory aims to accumulate the scientific base by the following research activities:
✓ Detail survey on municipal solid waste generation, demographics, 3R behavior, pro-environmental attitudes, lifestyle, and household expenditure in Japan and Vietnam
✓ Exploring influence factors and Bayesian modeling of waste generation and 3R behavior
✓ Political effect prediction on 3Rs and reliability verifi- cation
✓ Accuracy improvement on sales prediction of food items by Deep Learning toward food loss reduction
Study on the mechanism of environmental flower sex determination in plants and its adaptive significance

To establish and expand 3R good practices toward sustainable society, our laboratory tries some pilot studies including 3R promotion and effect measurement as the following activities:
✓ Experience-based activity for 3Rs in cooperation with trial dining event in downtown by gamification
✓ Development of beverage by returnable bottle with Carbon Footprint Ecolabel To enhance the public’s understanding on the effect of Reuse, the label indicated “When you discard in one, you discharge 430g-CO2e. When you reuse 5 times, you discharge 130g-CO2e in one and can decrease 69% of GHGs.
Research Area : Solid Waste Management and Recycling

- Asst. Prof.
HABUER
Analysis of material flow and environmental and resource impact for strategic management of End-of-life electronic and electrical equipment in China

In strategic end-of-life electrical and electronic equipment (EoL EEE) management, it has become important to not only avoid the negative environmental impacts but also enhance the positive effects of secondary resource utilization. This is especially true in emerging countries such as China, where medium- to long-term increases in the amount of EoL EEE generation are projected. In this study, we aim to assess the resource availability potential for EoL EEE recycling based on penetration scenarios for formal and/or informal treatment options for the strategic EoL-EEE management, including plans for appropriate capacities of recovery and treatment facilities to meet the requirement of proper waste treatment as well as to maximize secondary resource recovery.
Substance flow analysis of mercury in Malaysia
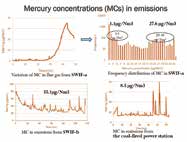
Mercury is a heavy metal of special concern because it has many serious impacts on human health and the environment. It can be found in many minerals, although cinnabar is the only ore being extracted for the principal product. For the appropriate management of mercury, sources of emissions and release, as well as the amounts released, need to be clarified. In this study, we aim to develop a mercury emissions inventory for Malaysia by measuring the actual emissions levels in two solid waste incineration facilities (SWIF-a and SWIF-b) and a coal-fired power station, as well as the mercury concentrations in the combustion residues and feedstock.
